The Unseen Efficiency: Why Plate Heat Exchangers Saves Energy for our Industry?
In the intricate dance of industrial processes, efficiency is paramount. Every degree of heat managed, every ounce of energy recovered, contributes to the bottom line and environmental sustainability. Among the myriad of thermal solutions, the plate heat exchanger stands out as a true champion of efficiency. These compact powerhouses are quietly revolutionizing how industries from HVAC to heavy manufacturing handle their thermal demands.
What Makes Plate Heat Exchangers So Indispensable?
The concept of heat exchange has been fundamental to human progress, from ancient heating systems to modern power plants. However, the plate heat exchanger, as we know it today, emerged from the 20th century’s drive for more compact, efficient, and versatile heat transfer solutions. Unlike older, bulkier designs, plate heat exchangers offer a significantly larger heat transfer surface area within a much smaller footprint. This innovation allows for rapid and highly effective thermal exchange, making them a cornerstone in applications demanding precision and energy recovery.
How Do Plate Heat Exchangers Work Their Magic?
At their core, plate heat exchangers consist of a series of thin, corrugated plates pressed together, creating intricate flow channels. Hot and cold fluids flow in alternating channels, separated only by the thin plate material. The clever design of the corrugations creates turbulence, ensuring that both fluids come into maximum contact with the plate surface, thereby maximizing the rate of heat transfer. This counter-current flow, combined with the large surface area, allows for extremely close temperature approaches, meaning the hot fluid can get very close to the cold fluid’s outlet temperature, recovering more energy.
What Are the Different Types of Plate Heat Exchangers?
While the core principle remains the same, plate heat exchangers come in various configurations to suit diverse industrial needs:
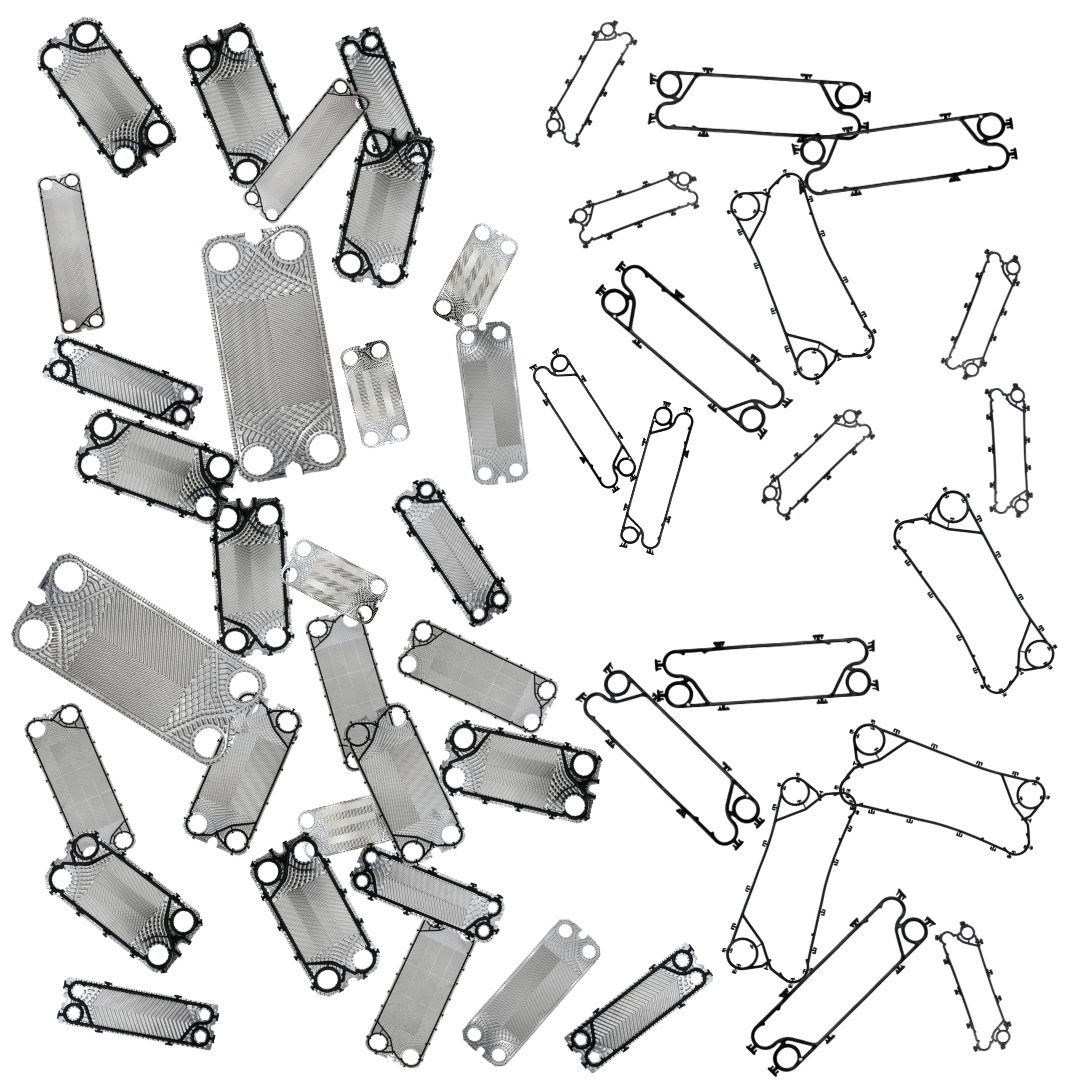
- Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers (GPHEs): These are the most common type, featuring removable plates sealed by gaskets. Their modular design allows for easy cleaning, inspection, and capacity expansion by simply adding or removing plates. This flexibility makes them ideal for applications where maintenance access is important or where process conditions might change.
- Welded Plate Heat Exchangers: For applications involving high pressures, extreme temperatures, or aggressive fluids where gaskets would be problematic, fully welded plate heat exchangers offer robust, leak-free performance. While not as easily expandable or cleanable on the fluid side as GPHEs, their durability is unmatched in demanding environments like petrochemicals or offshore platforms.
- Semi-Welded Plate Heat Exchangers: These offer a hybrid solution, with some plate pairs welded together and others sealed with gaskets. This design provides the strength of welded units for aggressive fluids on one side while retaining the serviceability of gaskets on the other, less aggressive fluid side.
- Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers: Compact and highly efficient, these units are permanently sealed using a brazing material. They are often used in refrigeration, HVAC, and smaller industrial applications where their minimal footprint and high thermal performance are advantageous.
Where Do Plate Heat Exchangers Shine in Industry?
The versatility of plate heat exchangers means they are found in nearly every sector that requires precise thermal management. Their ability to handle high heat loads in compact spaces makes them invaluable across a broad spectrum of applications:
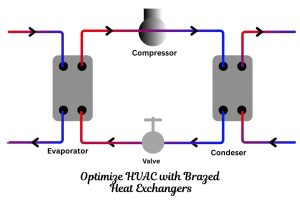
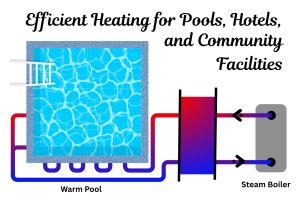
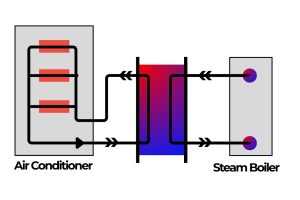
- HVAC and Refrigeration: For heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in commercial and industrial buildings, they efficiently transfer heat between chilled water, glycol, or refrigerant circuits.
- Food and Beverage: Sterilization, pasteurization, and cooling of products like milk, juice, beer, and sauces benefit from the hygienic design and efficient heat transfer.
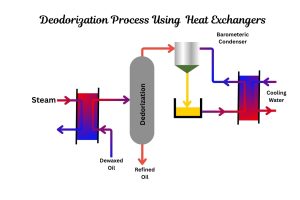
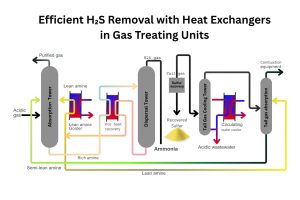
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical: They are crucial for reaction temperature control, solvent recovery, and condensing vapors, often dealing with corrosive or viscous fluids.
- Power Generation: Used in district heating, engine cooling, and heat recovery from exhaust gases, contributing to overall energy efficiency.
- Marine Applications: For cooling engine jacket water, lubricating oil, and central cooling systems on ships and offshore platforms.
- Heavy Industrial Processes: In industries like steel, mining, and pulp and paper, they manage process fluid temperatures and recover waste heat.
Even for larger capacity requirements, certain plate heat exchanger models are specifically engineered to manage high flow rates and significant thermal loads with exceptional efficiency. These units are designed with enhanced plate patterns and robust frames to ensure reliable operation under demanding industrial conditions, proving that compact design doesn’t compromise power.
What Common Mistakes Should You Avoid When Using Plate Heat Exchangers?
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your plate heat exchanger involves more than just initial installation. Awareness of common pitfalls can save significant time and cost:
- Neglecting Regular Cleaning: Over time, process fluids can leave deposits (fouling) on the plates, reducing heat transfer efficiency and increasing pressure drop. Scheduled cleaning is vital.
- Ignoring Gasket Integrity: Gaskets are critical for sealing and often the first point of failure. Age, high temperatures, and incompatible fluids can cause them to harden, crack, or leak. Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential.
- Over-Tightening During Reassembly: When performing maintenance, over-compressing the plate pack can permanently deform plates and damage gaskets, leading to chronic leakage and reduced performance. Always follow the manufacturer’s specified closing dimensions.
- Incorrect Plate Orientation: Each plate in a heat exchanger has a specific orientation to create the correct flow paths. Installing plates incorrectly can lead to poor performance, uneven flow distribution, and even internal leaks. Always refer to the assembly diagram.
- Using Non-Standard or Inferior Spare Parts: While tempting to cut costs, using gaskets or plates that aren’t precisely manufactured to the original specifications can compromise sealing, heat transfer, and the overall integrity of the unit. Stick to high-quality, compatible replacements.
- Ignoring Minor Leaks: Even a small drip can indicate a larger underlying issue that could escalate quickly into significant fluid loss, contamination, or equipment shutdown. Investigate and address all leaks promptly, distinguishing between external gasket leaks and potential internal plate perforations.
Where Do the Materials for Plate Heat Exchangers Come From?
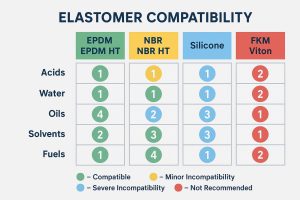
The durability and performance of plate heat exchangers heavily depend on the materials used in their construction. Plates are typically made from corrosion-resistant metals like stainless steel (304, 316), titanium, or specialized alloys such as Hastelloy or Incoloy, chosen based on the aggressiveness of the fluids and operating temperatures. Gaskets are manufactured from various elastomers (NBR, EPDM, Viton, etc.) selected for their chemical compatibility and temperature resistance. These high-grade materials are sourced globally from specialized manufacturers, ensuring the heat exchangers can withstand demanding industrial environments for years.
Frequently Asked Questions About Plate Heat Exchangers
What is the main advantage of a plate heat exchanger over a shell-and-tube type?
Plate heat exchangers typically offer higher thermal efficiency, a more compact footprint, and easier maintenance (especially gasketed types) compared to shell-and-tube exchangers. They are also better suited for close temperature approaches.
How do I know if my plate heat exchanger needs cleaning?
Signs that your plate heat exchanger may need cleaning include a decrease in heat transfer efficiency (e.g., fluids not reaching desired temperatures), an increase in pressure drop across the unit, or a noticeable decrease in flow rate.
Can plate heat exchangers handle very viscous fluids?
While plate heat exchangers are highly efficient, very viscous fluids can increase pressure drop and reduce heat transfer effectiveness. Specialized plate designs are available to optimize performance with more viscous media, but it’s important to consider fluid properties during the selection process.
What is the lifespan of plate heat exchanger gaskets?
The lifespan of gaskets varies significantly based on material, operating temperature, pressure, fluid chemistry, and usage frequency. Under optimal conditions, gaskets can last several years, but in harsh environments, they may require more frequent replacement, often every 1-3 years.
Is it possible to increase the capacity of my existing plate heat exchanger?
Yes, for gasketed plate heat exchangers, it is often possible to increase capacity by adding more plates within the existing frame, provided there is sufficient space and the frame is designed for expansion. This flexibility is a significant advantage of GPHEs. You can use our GPHE Selection tool to explore options.
Where can I find reliable spare parts for my plate heat exchanger?
Reliable spare parts, including plates and gaskets, are crucial for maintaining the performance and integrity of your heat exchanger. It’s important to source parts that match the exact specifications of your unit. For high-quality, equivalent spare parts, you can explore options at GPHE Spare Parts.
Ready to Enhance Your Thermal Management?
Optimizing your thermal processes with the right plate heat exchanger can lead to significant energy savings, improved operational efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs. Whether you are looking to acquire a new unit, replace worn components, or simply understand your current system better, expert guidance is invaluable.
Utilize our Heat Exchanger Calculator for quick estimates or contact us directly to discuss your specific requirements.
A Note from Heating Formula:
At Heating Formula, we specialize in supplying high-quality heat exchangers and spare parts that are equivalent to OEM standards. Our extensive range of products provides reliable and efficient solutions for various industries, ensuring your operations run smoothly with parts that offer perfect fit and performance, comparable to brands like Alfa Laval, Sondex, APV SPX, Funke, Schmidt, Vicarb, Gea, and Tranter.