The Smart Move: Why Closed-Loop Cooling with Plate Heat Exchangers is Your Competitive Edge
In today’s demanding industrial landscape, keeping critical equipment cool isn’t just a matter of performance—it’s a matter of survival. Overheating leads to production halts, premature equipment failure, and soaring operational costs. For decades, industries in Turkey, from burgeoning manufacturing plants to vital power generation facilities, have sought better ways to manage heat. The journey began with rudimentary, water-intensive open-loop systems, but as industrial processes grew in sophistication, so did the need for a smarter, more reliable solution.
Enter closed-loop cooling, a technology that has become the gold standard for efficiency and protection. When paired with the right technology—the Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger (GPHE)—this approach transforms thermal management from a costly necessity into a competitive advantage. This guide will break down why this combination is a game-changer for your operations.
What is a Closed-Loop Cooling System?
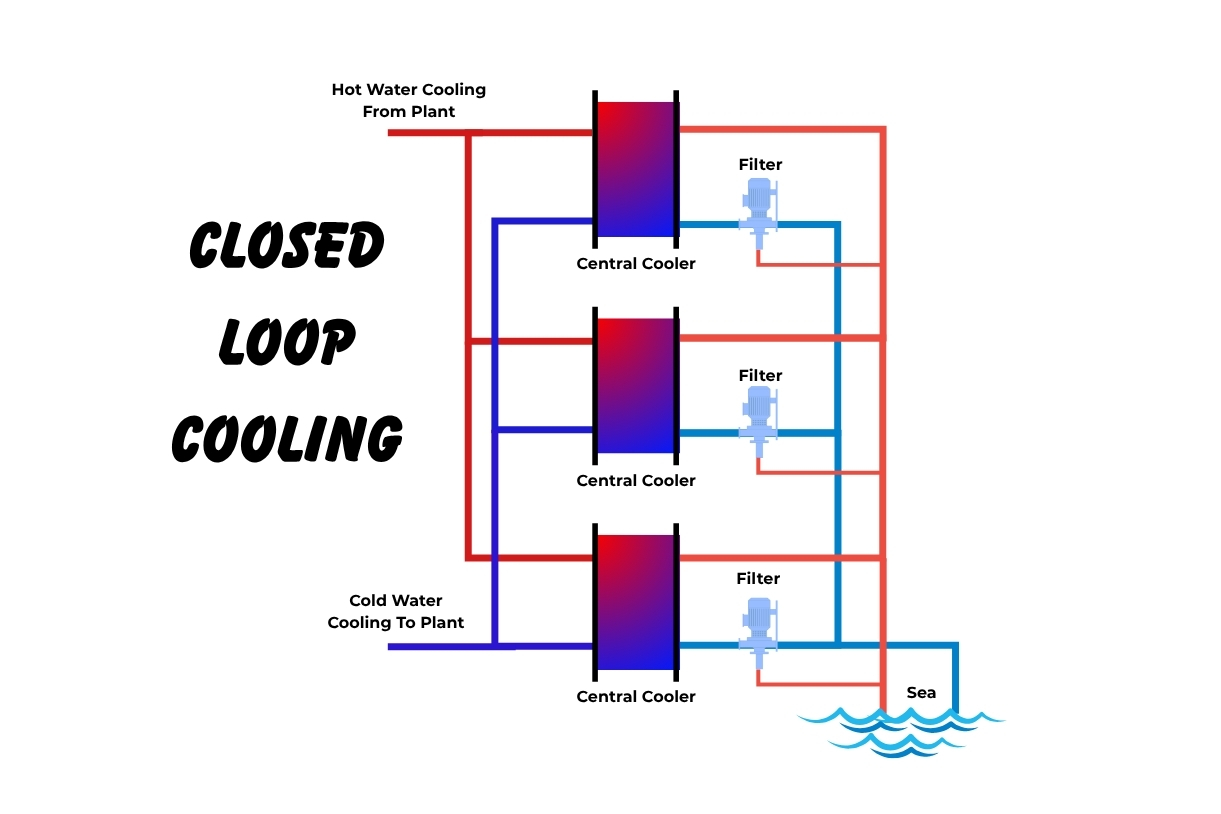
Think of a closed-loop cooling system as the radiator in your car. It uses a contained, clean coolant (like water or a water-glycol mixture) that circulates continuously to absorb heat from your process equipment and then transfers that heat away via a heat exchanger.
The alternative, an open-loop system (like a cooling tower), pulls in water from an external source, uses it to cool the equipment, and then exposes it to the atmosphere, leading to evaporation, contamination, and significant water loss.
A closed-loop system isolates your valuable machinery from the outside world. This prevents contaminants like dust, minerals, and biological growth from entering and fouling your process equipment, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.

Why are Plate Heat Exchangers the Heart of Modern Closed-Loop Systems?
While the concept is simple, the efficiency of a closed-loop system hinges on one critical component: the heat exchanger. This is where Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers (GPHEs) truly shine, far outperforming older technologies like bulky shell and tube exchangers.
GPHEs are built with a series of corrugated metal plates pressed together in a frame. The process fluid (hot) and the cooling fluid (cold) flow in alternating channels, creating an incredibly large surface area for heat transfer in a very small footprint. This design offers several key benefits:
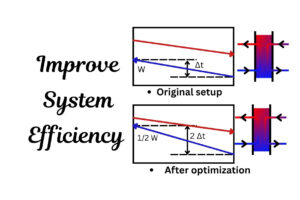
- Unmatched Thermal Efficiency: The high turbulence created by the corrugated plates allows for extremely efficient heat transfer. You can achieve a “close temperature approach,” meaning the temperature of the outgoing cold fluid can get very close to the temperature of the incoming hot fluid. This translates directly to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
- Compact Footprint: Plant floor space is a premium. A GPHE can provide the same or better cooling capacity as a shell-and-tube exchanger that is two to five times larger, freeing up valuable space for other equipment.
- Easy Maintenance and Adaptability: Downtime is the enemy of productivity. GPHEs are designed for easy servicing. You can simply open the frame, inspect every plate, and clean or replace components as needed. Furthermore, if your cooling needs change, you can easily add or remove plates to adjust the capacity—a level of flexibility unheard of with welded exchangers.

How Do Different Industries Benefit from This Technology?
The applications for closed-loop cooling with plate heat exchangers span nearly every major industry in Turkey and beyond:
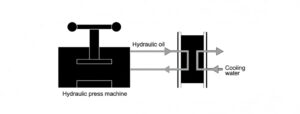
- Manufacturing & Automotive: Used to cool hydraulic oil, injection molding machines, welders, and quench furnaces. Precise temperature control ensures product quality and protects expensive machinery.
- Power Plants: Critical for cooling auxiliary systems like turbine lube oil, transformers, and generator sets. In these environments, reliability is non-negotiable, and GPHEs provide consistent performance under high stress.
- Food & Beverage Production: Maintaining precise temperatures is essential for processes like pasteurization, fermentation, and bottling. The sanitary design and easy cleaning of GPHEs prevent cross-contamination and ensure product safety.
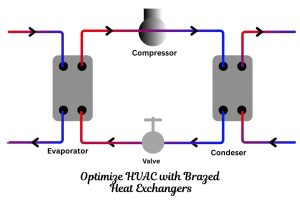
- HVAC & Data Centers: These systems are essential for district cooling and keeping server farms from overheating. The energy efficiency of GPHEs helps dramatically reduce the massive electricity costs associated with large-scale cooling.
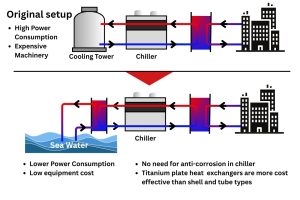
- Oil & Gas: Used in refineries for cooling hydrocarbons and other process fluids. The ability to use robust materials like Titanium or Hastelloy makes GPHEs suitable for handling corrosive media.

What Should You Consider Before Implementation?
Switching to a closed-loop system is a strategic decision. To maximize your return on investment, it’s crucial to get the details right. This involves more than just selecting a piece of equipment; it requires a holistic approach.
Referencing the principles of proper system design, you should focus on a few key areas. Proper sizing is paramount; an oversized unit is a waste of capital, while an undersized one will fail to meet your cooling demands, creating a bottleneck. It’s also vital to select the right materials for the plates and gaskets based on your specific process fluids to ensure longevity and prevent corrosion. Finally, never underestimate the cost of unplanned downtime. Planning for regular maintenance, made simple by the design of GPHEs, will save you from emergency repairs and costly production losses.
To make this process easier, you can use our Heat Exchanger Calculator to get an initial assessment of your needs.

Your Partner for Efficient Cooling: Heating Formula
A closed-loop cooling system powered by a high-efficiency gasketed plate heat exchanger is one of the smartest investments you can make for your facility. It reduces water consumption, protects your equipment, lowers energy bills, and minimizes downtime.
At Heating Formula, we specialize in providing tailored thermal solutions for Turkey’s leading industries. We understand that the right heat exchanger is not just a component—it’s the heart of your process. We offer a comprehensive range of solutions, including:
- Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers (GPHEs): Engineered for maximum efficiency and serviceability. Find the perfect fit with our GPHE Selection tool.
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers: For high-pressure and high-temperature applications where rugged reliability is key.
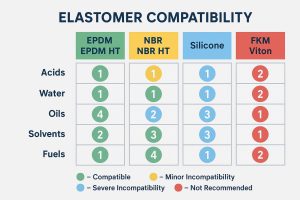
- High-Quality Spare Parts: We provide a vast inventory of GPHE spare parts, including plates and gaskets, to keep your operations running smoothly. Our parts are fully compatible with leading OEM brands like Alfa Laval, Sondex, APV SPX, Funke, Schmidt, Vicarb, Gea, and Tranter. We stock plates in 316/304 Stainless Steel, Titanium, C-276 Hastelloy, and 254 SMO, and gaskets in EPDM, NBR, and Viton to match any application.
Don’t let inefficient cooling dictate your bottom line. Contact Heating Formula today to discover how we can help you build a more reliable, efficient, and profitable operation.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What’s the main difference between open-loop and closed-loop cooling? An open-loop system, like a cooling tower, draws in external water, uses it once, and exposes it to the atmosphere, leading to contamination and water loss. A closed-loop system continuously circulates a clean, contained coolant, protecting equipment from fouling and conserving water.
2. How does a GPHE improve the efficiency of a closed-loop system? A Gasketed Plate Heat Exchanger (GPHE) has a large surface area and creates high turbulence, allowing for much more effective heat transfer in a smaller unit compared to other exchanger types. This means your cooling system uses less energy to achieve the required temperatures.
3. Can I use my existing water source with a closed-loop system? Yes. A plate heat exchanger acts as an isolator. You can use water from a river, lake, or cooling tower on one side of the exchanger to cool the clean, self-contained coolant on the other side. This protects your critical process equipment from any dirt, debris, or minerals in the source water.
4. How do I determine the right size for my cooling system’s heat exchanger? Proper sizing depends on your flow rates, start and end temperatures, fluid types, and allowable pressure drop. Using an online tool like our Heat Exchanger Calculator is a great starting point, followed by a consultation with our experts to finalize the design.
5. What are the signs that my heat exchanger gaskets need replacing? The most obvious sign is an external leak. Internally, aging gaskets can harden and lose their seal, leading to reduced performance or, in a worst-case scenario, mixing of the two fluids. Regular inspection and proactive replacement, as outlined in our maintenance guides, are key. If you need replacements, you can find OEM-quality options in our GPHE spare parts section.