Why 254 SMO is the Heat Exchanger’s Champion for Corrosive Applications
As a heat exchanger sales engineer, one of the most frequent challenges I encounter is specifying materials that can withstand aggressive, corrosive environments while maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency. In such demanding scenarios, one alloy consistently rises to the top: 254 SMO.
This article delves into the unique properties of 254 SMO (also known as UNS S31254), its advantages in heat exchanger applications, and the specific industries where it truly shines. We’ll also explore why investing in 254 SMO for your heat exchangers is a smart long-term decision.
What is 254 SMO and Why is it Special?
254 SMO is a high-alloy austenitic stainless steel, specifically designed for use in aggressive halide-containing environments, particularly those with high chloride concentrations. Its superior corrosion resistance comes from a carefully balanced composition, typically including:
- High Chromium (approx. 20%): Provides excellent general corrosion resistance.
- High Nickel (approx. 18%): Enhances stability of the austenitic structure and improves resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
- High Molybdenum (approx. 6%): This is the key element for exceptional resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich solutions.
- Nitrogen (approx. 0.2%): Further boosts pitting and crevice corrosion resistance and increases mechanical strength.
This unique combination gives 254 SMO a Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN) significantly higher than standard stainless steels like 304 or 316. A higher PREN indicates better resistance to localized corrosion, which is often the Achilles’ heel of heat exchangers in harsh conditions.
The Unmatched Advantages of 254 SMO in Heat Exchangers
When it comes to heat exchangers, 254 SMO offers a compelling array of benefits:
- Exceptional Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance: This is paramount for heat exchangers dealing with seawater, brackish water, or process fluids containing chlorides. Its high molybdenum and nitrogen content effectively combats these insidious forms of corrosion, which can quickly lead to leaks and equipment failure in lesser materials.
- Superior Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) Resistance: In applications involving chlorides and elevated temperatures, austenitic stainless steels can be susceptible to SCC. Its high nickel content provides enhanced resistance, ensuring greater operational safety and longevity.
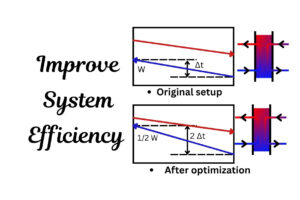
- High Mechanical Strength: The nitrogen addition not only aids corrosion resistance but also provides higher mechanical strength compared to conventional austenitic stainless steels. This can potentially allow for thinner plate designs, optimizing heat transfer and reducing material costs.
- Excellent Weldability: Despite its high alloy content, 254 SMO generally exhibits good weldability, which is crucial for the fabrication and repair of heat exchanger plates and frames.
- Reduced Fouling Tendency: While not entirely immune, its smooth surface finish and corrosion resistance can contribute to a reduced tendency for fouling compared to materials that corrode more readily. This translates to longer operating cycles and less frequent cleaning.
- Longer Lifespan and Reduced Downtime: By mitigating common corrosion mechanisms, 254 SMO heat exchangers offer significantly extended operational lifespans, leading to less frequent replacements and substantial reductions in costly downtime for maintenance and repairs.
Key Applications for 254 SMO Heat Exchangers
Based on its exceptional properties, 254 SMO is the material of choice for heat exchangers in a variety of industries where corrosive media are prevalent:
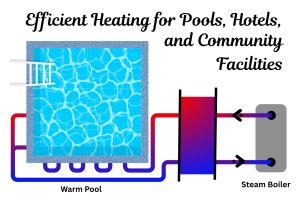
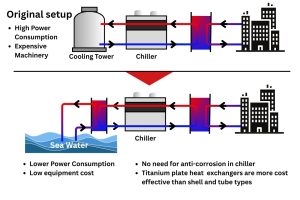
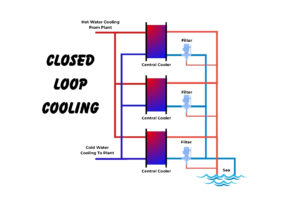
- Seawater and Brackish Water Cooling: This is perhaps the most prominent application. Industries like marine, offshore oil and gas, power generation, and district cooling extensively use seawater for cooling. Plate heat exchangers with this material are ideal for central cooling systems, lubricating oil cooling, and district cooling solutions utilizing seawater.
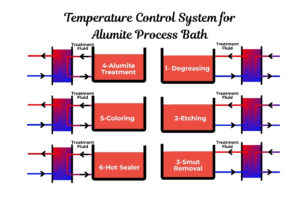
- Chemical Processing: Handling aggressive chemicals, especially those containing chlorides, requires robust materials. 254 SMO is used in various chemical applications, including waste heat recovery from condenser water and processes where highly corrosive substances are present.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: In certain stages of pulp and paper production, processes involve chloride-containing bleaching chemicals. 254 SMO can withstand these conditions, offering reliable heat transfer solutions.
- Mining Industry: Mining operations often involve process fluids with high concentrations of dissolved salts and abrasive particles. Its corrosion and erosion resistance make it suitable for various heat transfer duties in this sector.
- Pharmaceutical and Food Industries (Specific Applications): While 316L is common, some niche applications in these industries might involve highly aggressive cleaning agents or processes where 254 SMO’s enhanced corrosion resistance is beneficial.
- Desalination Plants: Critical for preheating and cooling streams in desalination processes where highly concentrated brines are present.
Sourcing and Manufacturing of 254 SMO Plates
Leading heat exchanger manufacturers are at the forefront of utilizing 254 SMO for their high-performance plate heat exchangers.
- One manufacturer offers 254 SMO as a plate material option for their gasketed plate heat exchangers, particularly for demanding applications where high corrosion resistance is paramount. They emphasize their extensive plate portfolio and ability to customize solutions for various applications.
- Another manufacturer offers 254 SMO (often referred to as 315J1 or specific high nickel alloys) as a plate material. They highlight their advanced pressing technology to manufacture these thin, high-performance plates, ensuring uniform deformation and maximized heat transmission area.
The manufacturing process for 254 SMO plates involves precision pressing and often features specialized plate patterns (like herringbone or specific corrugated designs) to maximize turbulence and heat transfer efficiency, while also mitigating fouling.
Addressing Common Problems and Ensuring Longevity
While 254 SMO is highly resistant, proper design, operation, and maintenance are still crucial to maximize its lifespan:
- Fouling: Even with its superior corrosion resistance, fouling can still occur, especially with certain fluid characteristics. Regular cleaning-in-place (CIP) with appropriate cleaning agents (e.g., specialized cleaner series tailored for specific scales) is recommended to maintain performance and extend service intervals.
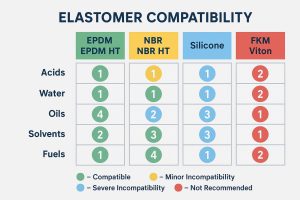
- Gasket Selection: While the plates are robust, the gaskets remain a critical consumable. It’s essential to select the correct gasket material (e.g., NBR, EPDM, or fluororubber) compatible with the specific operating temperatures and chemical media on both sides of the heat exchanger. Regular inspection and timely replacement of gaskets are vital to prevent leaks and maintain sealing performance.
- Flow Velocity and Pressure Drop: Optimized flow distribution and maintaining appropriate flow velocities are crucial to prevent erosion-corrosion, especially at plate contact points and near inlets. Manufacturers carefully design plate patterns to ensure uniform distribution and minimize dead zones.
- Impact Pressure/Water Hammering: Sudden pressure surges or water hammering can deform plates and lead to leaks or cracks. Proper system design with slow startups and shutdowns, and the inclusion of safety devices like relief valves, are essential to prevent such occurrences.
- Professional Maintenance: For optimal performance and extended life, I always recommend engaging with certified service providers for periodic inspections, cleaning, and replacement of parts. Services like “Full Service Package” ensure that your heat exchanger operates at its peak for years to come.
Conclusion
For applications demanding high resistance to localized corrosion, particularly in chloride-rich environments, 254 SMO stands out as an exceptional material for heat exchangers. Its unique composition delivers a powerful combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and performance. While the initial investment might be higher than for standard stainless steels, the extended lifespan, reduced downtime, and enhanced operational reliability offered by 254 SMO heat exchangers consistently deliver superior long-term value. For heat exchanger selection assistance, please visit our heat exchanger selection page. For information on spare parts, refer to our spare parts page. To get in touch, please visit our contact page.