How Can Nanofluids Improve Heat Transfer in Microprocessor Cooling Systems?
Introduction: Why Are Nanofluids Gaining Attention in Thermal Management?
The rapid advancement of technology has led to the development of smaller, more powerful microprocessors, which generate significant amounts of heat. Efficient heat removal is critical to prevent thermal damage and ensure optimal performance. Traditional cooling methods, such as air-cooled heat sinks, are often insufficient for modern high-performance processors. This has led to increased interest in nanofluids, which are fluids enhanced with nanoparticles to improve their thermal properties.
This article explores the use of Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) and Silver Oxide (AgO) nanofluids in cooling systems for microprocessors. The study compares the cooling performance of these nanofluids with traditional coolants like water and ethylene glycol. The goal is to minimize the base temperature of the heat sink and maximize heat transfer rates, ensuring efficient thermal management for high-heat-generating devices.
What Are Nanofluids, and How Do They Enhance Heat Transfer?
Nanofluids are created by dispersing nanoparticles, such as Aluminum Oxide or Silver Oxide, into a base fluid like water or ethylene glycol. These nanoparticles significantly enhance the thermal conductivity of the base fluid, leading to improved heat transfer rates.
Key Benefits of Nanofluids:
- Higher Thermal Conductivity: Nanofluids can transfer heat more efficiently than traditional coolants.
- Improved Cooling Rates: Nanofluids reduce the base temperature of heat sinks more effectively.
- Energy Efficiency: Using nanofluids can conserve energy, making them an attractive option for thermal management.
How Was the Experimental Setup Designed?
Heat Sink and Cooling System
The experimental setup included a pin-fin heat sink manufactured using a CNC machine. The heat sink was made of copper and attached to a heating block that simulated a microprocessor. The system also included a Heating Formula radiator, a brushless DC pump, and a flow meter to measure the coolant flow rate.
Nanofluid Preparation
The study used three types of nanofluids:
- Al₂O₃-H₂O: Aluminum Oxide nanoparticles dispersed in deionized water.
- Al₂O₃-EG: Aluminum Oxide nanoparticles dispersed in ethylene glycol.
- AgO-H₂O: Silver Oxide nanoparticles dispersed in deionized water.
The volumetric concentrations of the nanoparticles were kept low (0.001% to 0.002%) to ensure stability and avoid clogging in the cooling system.
What Were the Key Findings of the Study?
Heat Transfer Performance
The study compared the heat transfer rates of nanofluids with traditional coolants like water. The results showed that:
- Al₂O₃-H₂O nanofluid improved heat transfer by 2.74% compared to water.
- Al₂O₃-EG nanofluid showed a 9.12% improvement in heat transfer.
- AgO-H₂O nanofluid outperformed both, with a 15.57% increase in heat transfer rate.
Base Temperature Reduction
The base temperature of the heat sink, which is critical for microprocessor performance, was significantly reduced using nanofluids:
- Al₂O₃-H₂O reduced the base temperature by 3.61% compared to water.
- AgO-H₂O showed the most significant reduction, with a 3.17% improvement over water.
Stability of Nanofluids
One of the challenges of using nanofluids is their stability. The study found that using a two-step preparation method and ultrasonication at high frequencies (42 kHz) improved the stability of nanofluids to up to 48 hours at 70°C.
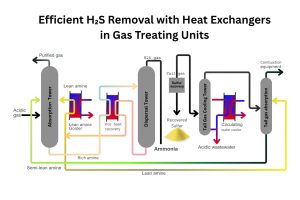
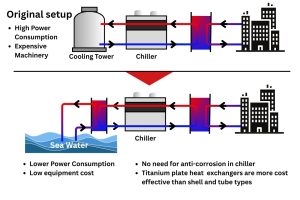
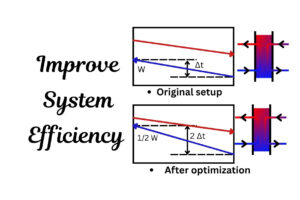
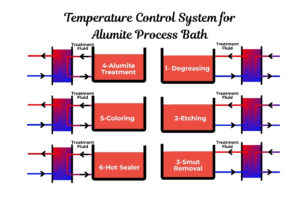
How Can These Findings Benefit Plate Heat Exchanger Systems?
The findings of this study have significant implications for plate heat exchanger systems, which are widely used in industrial and commercial applications. By incorporating nanofluids into these systems, businesses can achieve:
- Higher Heat Transfer Efficiency: Nanofluids can enhance the thermal performance of plate heat exchangers, leading to better cooling and energy savings.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Improved heat transfer rates can lower energy consumption and reduce operational expenses.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Efficient cooling reduces thermal stress on equipment, prolonging its lifespan.
At Heating Formula, we specialize in providing high-quality materials for plate heat exchangers, ensuring optimal thermal management for your systems. Our products are designed to meet the demands of modern cooling applications, offering superior performance and reliability.
Conclusion: What Does the Future Hold for Nanofluids in Thermal Management?
The study demonstrates that nanofluids, particularly AgO-H₂O, offer significant improvements in heat transfer and cooling efficiency compared to traditional coolants. These findings highlight the potential of nanofluids to revolutionize thermal management in high-heat-generating devices, including microprocessors and plate heat exchangers.
However, challenges such as stability and cost need to be addressed before nanofluids can be widely adopted. Future research should focus on improving the stability of nanofluids and developing cost-effective production methods.
For businesses looking to enhance their cooling systems, Heating Formula offers cutting-edge solutions for plate heat exchangers, ensuring efficient and reliable thermal management.
About Heating Formula
At Heating Formula, we are committed to providing innovative solutions for thermal management. Our range of plate heat exchanger materials is designed to meet the highest standards of performance and durability. Whether you’re cooling a microprocessor or managing heat in an industrial process, Heating Formula has the products and expertise to help you achieve optimal results.
References
- Eapen J, Rusconi R, Piazza R, Yip S (2010) The Classical Nature of Thermal Conduction in Nanofluids. J Heat Transf 132(10):102402
- Timofeeva EV, Yu W, France DM, Singh D, Routbort JL (2011) Nanofluids for heat transfer: an engineering approach. Nanoscale Res Lett 6(1):182
- Yu W, Xie H (2012) A Review on Nanofluids: Preparation, Stability Mechanisms, and Applications. J Nanomater 2012:1–17
- Gupta H, Agrawal G, Mathur J (2012) An overview of Nanofluids: A new media towards green environment. Int J Environmental Sci 31(1):433–440
By leveraging the latest advancements in nanofluid technology, Heating Formula is paving the way for more efficient and sustainable thermal management solutions.